HP Prime and TI-84 Plus CE: Circle Determined by Three Points
The programs
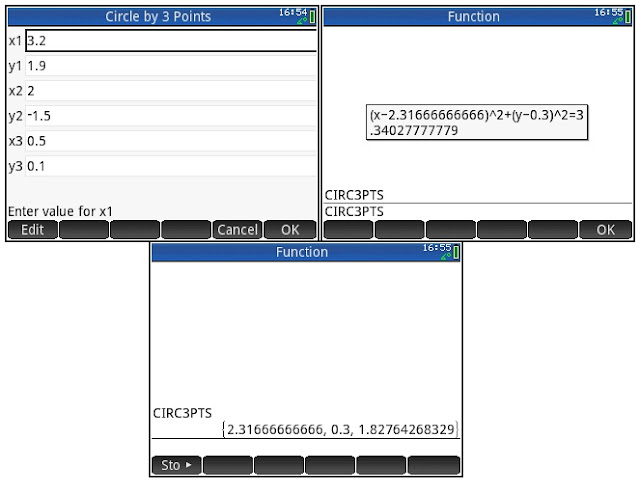
CIRC3PTS (HP Prime) and CIRCBY3 (TI-84 Plus CE) calculate the center and radius
of a circle given three points (x1, y1), (x2, y2), and (x3, y3). The HP Prime will display the equation
(x-x0)^2 + (y-y0)^2 = r^2 in a message box.
Both versions will return a list {x0, y0, r}.
The center
point (x0, y0) is calculated by:
[ [ x0 ] [ y0 ]
] =
[ [ x1 – x3, y1
– y3 ] [ x1 – x2, y1 – y2 ] ]^-1 * [ [ a ] [ b ] ]
Where:
a = 0.5 * ( (x1
– x3)*(x1 + x3) + (y1 – y3)*(y1 + y3) )
b = 0.5 * ( (x1
– x2)*(x1 + x2) + (y1 – y2)*(y1 + y2) )
r = √( (x1 – x0)^2
+ (y1 – y0)^2 )
HP Prime Program: CIRC3PTS
EXPORT CIRC3PTS()
BEGIN
// 2016-10-09
// Circle by 3 Points
LOCAL x1,y1,x2,y2;
LOCAL x3,y3,x0,y0;
LOCAL a,b,m,r;
LOCAL str;
// Input box
INPUT({x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3},
"Circle by 3 Points",
{"x1","y1","x2","y2",
"x3","y3"});
// Calculation
a:=0.5*((x1-x3)*(x1+x3)+
(y1-y3)*(y1+y3));
b:=0.5*((x1-x2)*(x1+x2)+
(y1-y2)*(y1+y2));
m:=[[x1-x3,y1-y3],[x1-x2,y1-y2]]^-1
*[[a],[b]];
x0:=m(1,1); y0:=m(2,1);
r:=(x1-x0)^2+(y1-y0)^2;
// build string
str:="(x-"+x0+")^2+(y-"+y0+
")^2="+r;
MSGBOX(str);
RETURN {x0,y0,√r};
END;
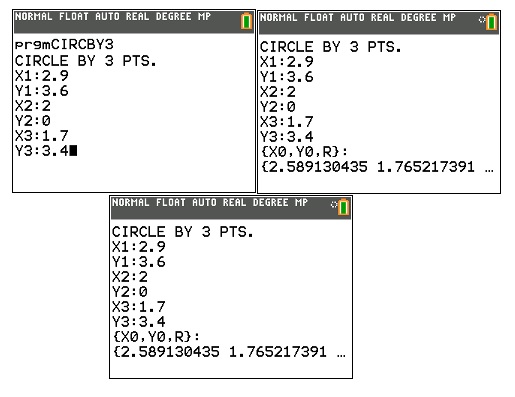
TI-84 Plus Program: CIRCBY3
Disp "CIRCLE BY
3 PTS."
Input
"X1:",D
Input
"Y1:",E
Input
"X2:",F
Input
"Y2:",G
Input
"X3:",H
Input
"Y3:",I
0.5*((D-H)*(D+H)+(E-I)*(E+I))→A
0.5*((D-F)*(D+F)+(E-G)*(E+G))→B
[[D-H,E-I][D-F,E-G]]^-1*[[A][B]]→[A]
[A](1,1)→X
[A](2,1)→Y
√((D-X)²+(E-Y)²)→R
Disp
"{X0,Y0,R}:"
Pause {X,Y,R}
Test Example:
(x1, y1): (2, 4)
(x2, y2): (0, 2)
(x3, y3): (-1, 3)
Result:
x0 = 0.5
y0 = 3.5
r = 1.58113883008
(x – 0.5)^2 +
(y – 3.5)^2 = 2.5
Source:
“Circle
Determined by Three Applications” HP-34C Mathematics Applications. Hewlett Packard, 1979
This blog is
property of Edward Shore, 2016.